Colour Doppler Imaging
Colour Doppler Imaging (CDI) is an advanced ultrasound technique used to visualize and assess blood flow within the body’s blood vessels. By combining traditional ultrasound imaging with Doppler technology, CDI provides detailed information about the speed and direction of blood flow, enhancing diagnostic capabilities in various medical fields.
How Colour Doppler Imaging Works
Colour Doppler Imaging uses a transducer to emit high-frequency sound waves into the body. These sound waves bounce off moving red blood cells within blood vessels, and the returning echoes are captured and analyzed. The Doppler effect, which shifts the frequency of the sound waves based on the movement of the blood cells, is used to determine the velocity and direction of blood flow. These measurements are then displayed as color-coded images on a monitor: typically, red indicates blood flow towards the transducer, and blue indicates flow away from it. The intensity of the color represents the speed of the blood flow.
Clinical Applications
Cardiology
In cardiology, Colour Doppler Imaging is essential for evaluating blood flow in the heart and major arteries. It helps diagnose conditions such as valve stenosis or regurgitation, congenital heart defects, and myocardial infarction. By visualizing the flow of blood through the heart chambers and valves, CDI provides valuable information about cardiac function and efficiency.
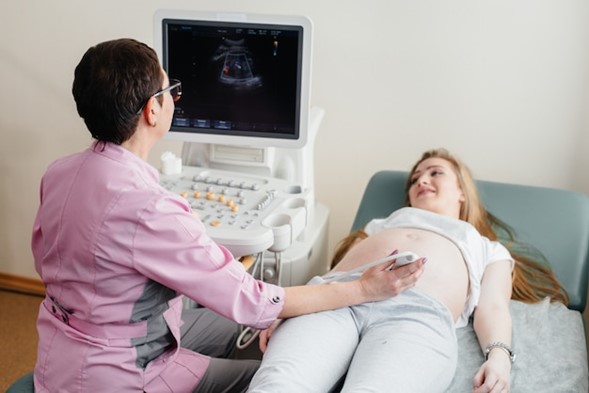
Obstetrics
During pregnancy, CDI is used to monitor the health of both the mother and the fetus. It assesses blood flow in the umbilical cord, placenta, and fetal organs, ensuring that the fetus is receiving adequate oxygen and nutrients. CDI can detect conditions like umbilical cord knots or restricted blood flow, which could lead to fetal distress.
Vascular Medicine
Colour Doppler Imaging is widely used to evaluate blood flow in peripheral arteries and veins. It helps diagnose conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), peripheral artery disease (PAD), and varicose veins. By visualizing blood flow patterns, CDI can identify blockages, narrowing, or abnormal flow, guiding treatment decisions.
Neurology
In neurology, CDI is used to assess blood flow in the carotid arteries, which supply blood to the brain. This is crucial in detecting carotid artery stenosis, a major risk factor for stroke. CDI can also evaluate intracranial vessels, providing insights into conditions such as aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations.
Advantages of Colour Doppler Imaging
Non-Invasive and Safe
Colour Doppler Imaging is a non-invasive procedure that does not involve radiation, making it safe for repeated use. It is also relatively quick and can be performed on an outpatient basis, providing immediate results.
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
By providing real-time images of blood flow, CDI enhances the accuracy of diagnoses. It allows for the visualization of dynamic blood flow patterns, which is crucial for assessing the severity and nature of vascular conditions.
Versatility
CDI can be applied to various parts of the body, including the heart, blood vessels, and organs. Its versatility makes it an invaluable tool across multiple medical specialties, from cardiology and obstetrics to neurology and vascular medicine.
Limitations
Despite its many advantages, Colour Doppler Imaging has limitations. The quality of the images can be affected by the patient’s body habitus and the skill of the technician. Additionally, CDI may not provide detailed information about the structure of blood vessels or tissues, sometimes requiring complementary imaging techniques such as MRI or CT angiography for comprehensive evaluation.
Integration with Other Diagnostic Tools
Colour Doppler Imaging is often used alongside other imaging modalities to provide a comprehensive assessment. For example, combining CDI with echocardiography in cardiology or with standard ultrasound in obstetrics enhances diagnostic precision and patient care.

