Fetal Echo Cardiography
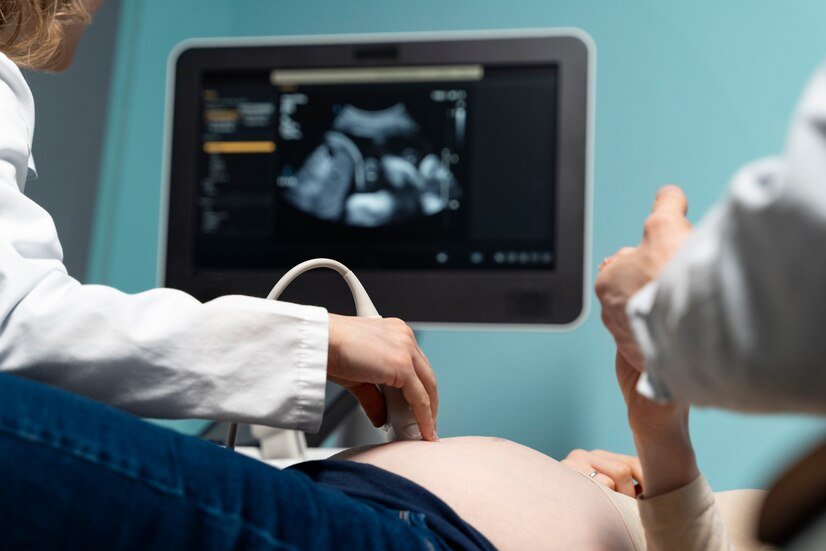
Fetal echocardiography is a specialized ultrasound procedure used to assess the structure and function of a developing fetus’s heart. This detailed imaging test is typically performed during the second trimester of pregnancy, between 18 and 24 weeks, and is crucial for detecting congenital heart defects and other cardiac abnormalities early in pregnancy.
How Fetal Echocardiography Works
Fetal echocardiography employs high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of the fetal heart. A transducer is placed on the mother’s abdomen, which emits sound waves that bounce off the fetal heart structures and return to the transducer. These echoes are then processed to form real-time images of the heart’s anatomy and blood flow patterns. The procedure is non-invasive and typically lasts between 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the complexity of the heart’s anatomy and the position of the fetus.
Indications for Fetal Echocardiography
High-Risk Pregnancies
Fetal echocardiography is often recommended for high-risk pregnancies where there is an increased likelihood of congenital heart defects. Indications for this test include:
- A family history of congenital heart disease.
- Abnormal results from routine prenatal ultrasounds.
- Maternal conditions such as diabetes, lupus, or phenylketonuria (PKU).
- Exposure to certain medications or infections during pregnancy known to increase the risk of heart defects.
- Chromosomal abnormalities detected through other prenatal tests, such as Down syndrome.
Suspicious Findings
If a routine prenatal ultrasound detects potential cardiac anomalies or if there is an abnormal fetal heart rhythm, a more detailed examination through fetal echocardiography is warranted.
Clinical Applications
Diagnosing Congenital Heart Defects
Fetal echocardiography can identify a wide range of congenital heart defects, such as ventricular septal defects, atrial septal defects, tetralogy of Fallot, and transposition of the great arteries. Early diagnosis allows for better planning and management of the pregnancy and delivery, and for immediate postnatal care.
Monitoring Fetal Heart Function
This imaging test is also used to monitor the function of the fetal heart, ensuring it is pumping blood effectively. It assesses the heart’s chambers, valves, and major blood vessels, providing detailed information about the fetal cardiovascular system’s overall health.
Planning for Interventions
In cases where a significant heart defect is detected, fetal echocardiography aids in planning necessary interventions, either during pregnancy or immediately after birth. This might include the need for specialized care during delivery or early surgical interventions.
Advantages of Fetal Echocardiography
Non-Invasive and Safe
Fetal echocardiography is a non-invasive procedure that does not involve radiation, making it safe for both the mother and the fetus. It provides critical information without posing risks associated with more invasive diagnostic techniques.
Detailed Cardiac Assessment
This test offers a comprehensive view of the fetal heart, allowing for the detection of subtle abnormalities that might not be visible with standard prenatal ultrasounds. It provides high-resolution images and detailed functional assessments, contributing to accurate diagnoses.
Limitations
Despite its many advantages, fetal echocardiography has limitations. The quality of the images can be affected by factors such as fetal position, maternal obesity, or low amniotic fluid levels. Additionally, while fetal echocardiography can detect most structural heart defects, it may not always predict the severity of the condition after birth or detect all minor abnormalities.
Integration with Other Prenatal Care
Fetal echocardiography is often part of a comprehensive prenatal care plan, integrating with other diagnostic tools and assessments. It complements genetic testing, routine ultrasounds, and maternal-fetal medicine consultations to provide a holistic view of fetal health and development.

